
E-coat technology revolutionizes industrial applications by providing a protective layer against corrosion. High-build edge e-coat enhances this protection with thicker finishes. It focuses on areas prone to wear, ensuring durability. High-build e-coat systems offer superior coverage and adhesion.
High-edge build e-coat technology optimizes performance in challenging designs. Modern high-build e-coat technology achieves thicker coatings with fewer applications. It also ensures longevity and aesthetic appeal. E-coat technology remains essential for various industries and continues to evolve.
High-build e-coat systems provide unmatched durability.
Historical Context of E-Coating Technology
E-coating technology began in the mid-20th century. The automotive industry sought solutions for corrosion protection, so engineers developed e-coating as an innovative method. This technology used electrical currents to apply paint, ensuring even coverage on metal surfaces.
Manufacturers quickly adopted e-coating because of its efficiency. Compared to traditional painting, the method reduced waste and improved adhesion and durability.
Evolution of E-Coating Techniques
The evolution of e-coating techniques advanced rapidly. Researchers focused on improving coating thickness. High-build edge e-coat emerged as a significant development. This technique targeted areas prone to wear and tear.
Engineers refined application methods for better results. Innovations included more efficient dipping processes. These advancements reduced the number of required applications.
The automotive and aerospace industries benefited from its enhanced protection and longevity.
Understanding High-Build Edge E-Coat
High-build edge e-coat represents an advanced form of electrocoating. This technology focuses on applying a thicker layer of protective coating, targeting areas that experience high wear and tear.
Engineers developed this method to enhance durability. Its coating ensures superior coverage on sharp edges and corners, increasing corrosion resistance.
The technology achieves a uniform finish with fewer applications, resulting in a more efficient coating process.
Comparison with Traditional E-Coating
Traditional e-coating applies a thinner layer of paint, often requiring multiple applications for adequate coverage. High-build e-coat uses fewer application cycles, reducing time and costs in industrial processes. The advanced technique offers better protection for complex designs.
Traditional methods may struggle to cover intricate parts. High-build e-coat provides consistent thickness, leading to improved product longevity and performance.
High-Build Edge E-Coat Process
| Feature |
Description |
Advantages |
Benefits |
| Process |
Electrostatic application of a paint coating to a metal substrate using an electric current |
Efficient, controlled application |
Uniform coating, especially in complex geometries |
| Coating |
Typically, a cationic resin-based paint |
Excellent corrosion resistance, high film thickness |
Enhanced durability, protection against environmental factors |
| Application |
Parts are immersed in a paint bath, and a current is applied |
Automated process, high throughput |
Reduced labor costs, improved consistency |
| Curing |
The coated parts are heated to cure the paint film |
Controlled curing process |
Optimal film properties, enhanced adhesion |
| Edge Coverage |
Designed to provide superior coverage on sharp edges and corners |
Prevents corrosion initiation at vulnerable points |
Improved overall part lifespan |
| Adhesion |
Strong adhesion to the metal substrate |
Durable coating, resistant to peeling or delamination |
Enhanced part performance, reduced maintenance |
| Environmental Impact |
Lov VOC emissions compared to traditional painting methods |
Environmentally friendly, complies with regulations |
Reduced environmental footprint |
| Applications |
Automotive components, industrial machinery, and appliances |
Versatile application, suitable for various industries |
Wide range of potential uses |
Current Applications of High-Build Edge E-Coat
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies on a high-build edge e-coat for superior corrosion protection. Engineers use this technology to coat chassis components because its thicker coating ensures durability in harsh environments.
High-build edge e-coat reduces maintenance needs, enabling manufacturers to achieve longer-lasting vehicles. The process also enhances the aesthetic appeal of car parts.
Aerospace Applications
Aerospace applications demand high-performance coatings. High-build edge e-coat meets these requirements. Engineers apply this technology to aircraft components.
The coating provides excellent protection against extreme conditions and increases the lifespan of aerospace parts, supporting aviation safety and reliability.
Consumer Goods
High-build edge e-coat benefits consumer goods by enhancing product longevity. Manufacturers use this coating on appliances and electronics. The protective layer prevents rust and wear, and consumers enjoy products that maintain their appearance.
High-build edge e-coat adds value to everyday items, ensuring quality and user satisfaction.
Technological Advancements in High-Build Edge E-Coat
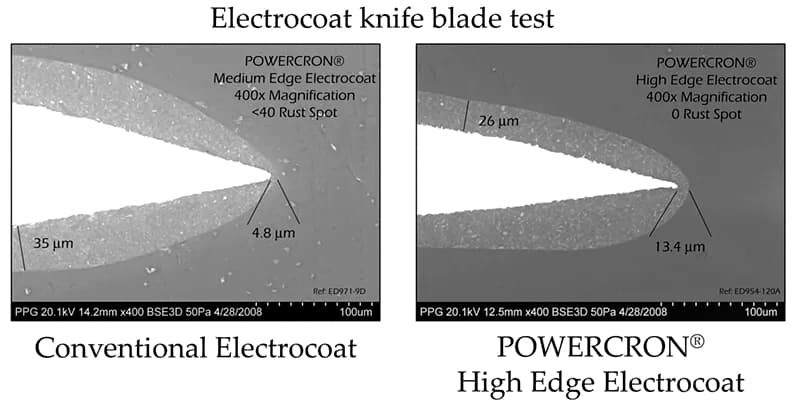 Modern high-build e-coat materials have transformed the industry. Early e-coat systems relied on basic formulations, which offered limited corrosion resistance. High-build e-coats introduced advancements in material science.
Modern high-build e-coat materials have transformed the industry. Early e-coat systems relied on basic formulations, which offered limited corrosion resistance. High-build e-coats introduced advancements in material science.
Engineers developed new polymers and resins, which enhanced durability and coverage. Manufacturers sought better performance and longevity as the demand for high-build e-coat materials increased. Modern High-Build materials provide superior protection.
The advancements in materials improved the coating process. The impact of these innovations is clear in product quality.
Improvements in Application Techniques
The application process of modern high-build e-coat has seen significant advancements. Early techniques required time-consuming, costly, and multiple steps. Modern High-Build systems simplified the process, and engineers optimized the application methods.
The improvements led to more efficient curing, which made culturing high-build e-coats faster and more reliable. The impact of these advancements is substantial, making the future of the high-build e-coat look promising. Manufacturers achieve consistent results with fewer resources, and advancements in application techniques enhance productivity.
The future of high-build e-coat continues to evolve.
Benefits of High-Build Edge E-Coat for Durability
High-build e-coat technology provides superior corrosion resistance. Engineers design this coating to protect metal surfaces from harsh environments, with the thicker layer acting as a barrier against moisture and chemicals. Industries benefit from reduced rust and degradation.
The technology ensures that products maintain their integrity. Manufacturers achieve longer-lasting components with this advanced coating.
Increased Longevity of Products
High-build e-coat significantly extends the lifespan of products—the robust coating shields items from wear and tear. Industries experience fewer failures and replacements. This durability leads to cost savings in maintenance and repairs. Consumers enjoy products that keep functionality and appearance. The technology enhances the value and reliability of various goods.
Challenges in Implementing High-Build Edge E-Coat
High-build edge e-coat technology faces technical challenges. Engineers encounter difficulties achieving uniform thickness: complex shapes and sharp edges present obstacles. The coating process requires precise control from variations in electrical conductivity affecting the results.
Engineers must address these issues for optimal performance. Equipment limitations hinder the application process because high-build e-coat demands advanced machinery. Consistency in application remains challenging, and engineers strive to improve techniques for better outcomes.
Cost Considerations
Implementing a high-build e-coat involves significant costs. The initial investment in equipment is substantial because of expensive specialized machinery, and the cost of materials impacts overall expenditure. Other cost considerations include:
- High-quality polymers and resins are essential.
- Equipment maintenance adds to operational costs.
- Training personnel requires additional resources.
The benefits of durability offset some expenses, and long-term savings justify the initial investment.
Future Prospects of High-Build Edge E-Coat
High-build edge e-coat technology continues to evolve. New trends in the industry focus on improving efficiency. Manufacturers explore ways to reduce application time. Innovations in materials lead to better performance. Engineers develop coatings with enhanced properties—and the demand for eco-friendly solutions increases.
Companies invest in research for sustainable options. The market for high-build edge e-coats is expanding globally. Industries seek advanced coatings for complex designs. The future promises more versatile applications.
Potential for Sustainability
Sustainability has become a priority in the coating industry. High-build edge e-coat offers potential for eco-friendly practices. Engineers work on reducing waste during production. Using recyclable materials gains attention. Manufacturers aim to lower energy consumption.
The development of water-based coatings progresses. These efforts contribute to environmental protection. Sustainable practices enhance brand reputation. Consumers prefer products with minimal environmental impact. The shift toward sustainability drives innovation.
In Sum
High-build edge e-coat plays a crucial role in enhancing product durability. The technology provides superior corrosion resistance and extends the lifespan of components. Industries benefit from reduced maintenance costs and improved product performance.
Future developments in high-build edge e-coat drive innovation across various sectors. Advancements in materials and application techniques promise more efficient and sustainable solutions. This technology's ongoing evolution continues to positively impact industries, ensuring products remain reliable and long-lasting.